Here are two amazing picture books to read to celebrate the start of fall!
One Leaf, Two Leaves, Count with Me!
Author: John Micklos, Jr.
Illustrator: Clive McFarland
Published September 5th, 2017 by Nancy Paulsen Books
Summary: This playful counting book shares the colorful highlights of the four seasons in charming illustrations.
Count your way through the seasons! In spring, the tree’s leaves appear, one by one. By summer, there’s a glorious canopy. And when autumn winds blow, leaves fly from the tree, one after another, leading us into winter. There’s a world of activity to spy in and around this beautiful tree as the wild creatures, and one little boy, celebrate the cycles of nature. As little ones count leaves, look for animals, and enjoy the changing seasonal landscape, bouncy rhymes and bold illustrations make learning to count easy–corresponding numerals reinforcing the learning fun.
My Thoughts: I think Micklos was quite clever in incorporating nature/seasons and counting into one book. This allows it to be used for multiple purposes in a classroom. Also, rarely do counting books count backwards, so I think it is nice that the book counts to ten and back. I also was impressed with how this non-narrative picture book told such a cute story of a young boy, his tree, and the animals that live in the tree. And the illustrations are so fun! I love the style of art. It is colorful, collage-looking, and just so friendly looking. I know this is a book that teachers, parents, and kids are going to definitely love!
Flagged Passages:
Autumn: A Pop-Up Book
Author and Illustrator: David A. Carter
Published August 29th, 2017 by Harry N. Abrams
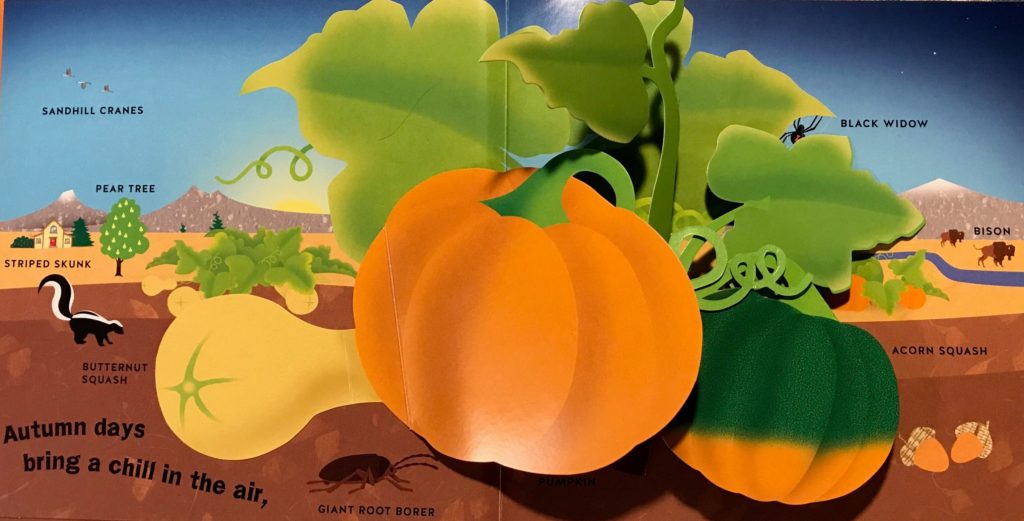
Summary: Just in time for autumn, David A. Carter delivers the third book in his pop-up book series about the seasons. Each spread has a brief verse and depicts flora and fauna commonly found during the fall. Pictures of turkeys, wheat, pumpkins, sage, and more are labeled with simple text, making the book easy for young readers to understand and enjoy.
David A. Carter is an American author and illustrator. He is best known for his pop-up books for both children and adults. David Carter’s Bugs series has sold more than six million copies. He lives in Auburn, California. Visit Carter at cartermultimedia.us.com.
My Thoughts: I am fascinated by pop-up books, and David A. Carter may be one of the best I’ve ever witnessed. Check out his website or search his name on You Tube to see some of his brilliant work. And I know that kids love his work because one of Trent’s favorite books right now is Spot the Dot by Carter, so I know he is going to love Autumn also. Carter’s work is so intricate and detailed, and Autumn specifically includes so many different components to check out–it is a piece of art.
Flagged Passages: I could not find a professional photo of the book, so please forgive my amateur pop-up book photography, but I knew you needed to see a spread from this beautiful book. The pumpkins, leaves, and vines are all pop-up.
Both Recommended For: